// This code was adapted from the 'button' example
// given to us in class! Especially regarding the
// serial communication functions in my code, that was
// taken from the 'button' example. The rest of the code
// is my own!
// Set the baud rate. This must match the number in Arduino’s
// Serial.begin() function.
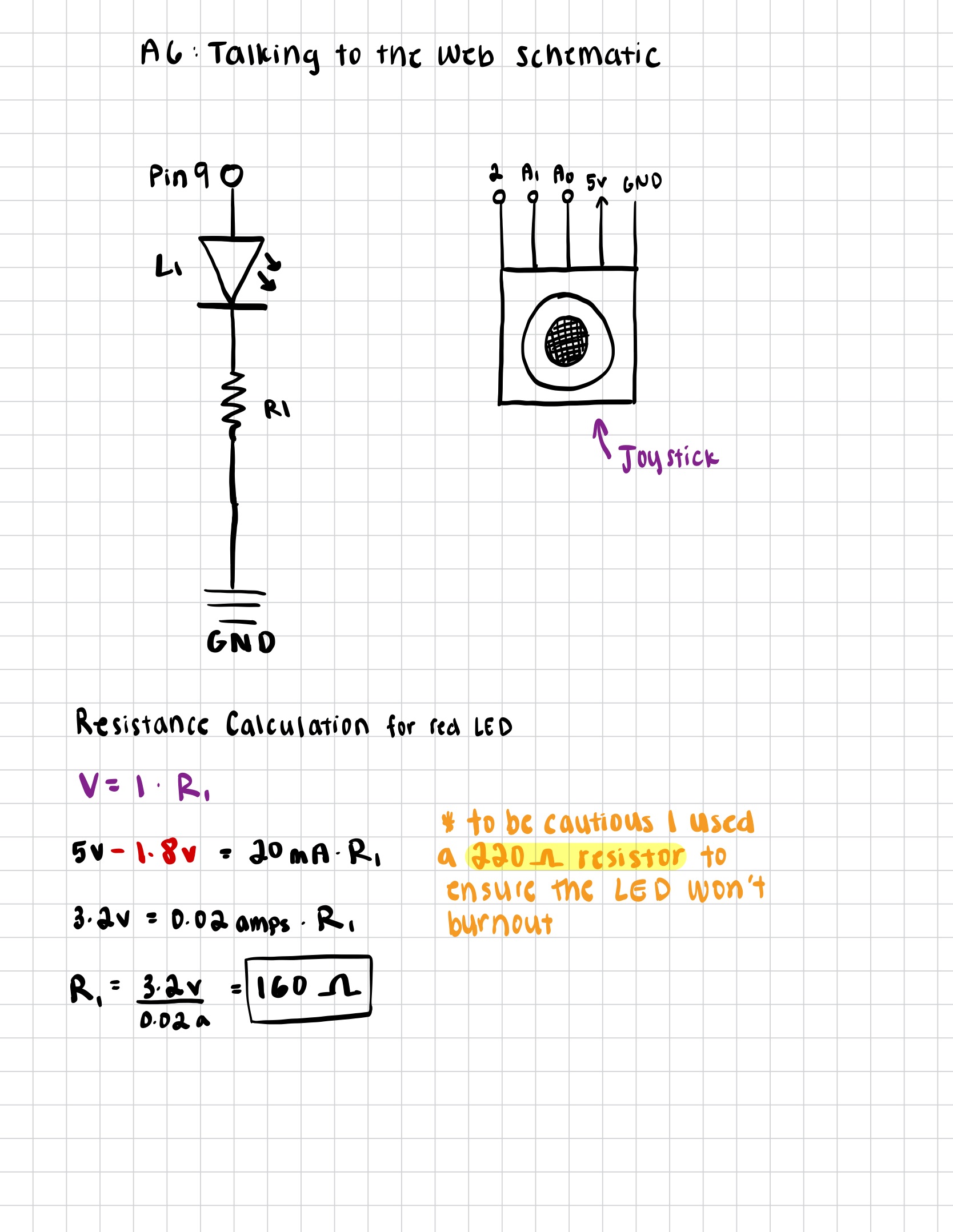
const BAUD_RATE = 9600;
// Variables for the serial port and the “Connect to Arduino” button.
let port;
let connectBtn;
// Default joystick values (center position).
let xVal = 512;
let yVal = 512;
// Variables for the spaceship’s position on the canvas.
let shipX, shipY;
// True/false variable that remembers whether the ship is
// touching an obstacle or not.
let collision = false;
function setup() {
setupSerial(); // Create the serial port and connect button.
createCanvas(800, 600); // Set the size of the game window.
// Start the spaceship in the middle of the screen.
shipX = width / 2;
shipY = height / 2;
}
function draw() {
// Check whether the Arduino is connected.
const portIsOpen = checkPort();
// If not connected, stop the game from running.
if (!portIsOpen) return;
// Read any new line of data from Arduino
let str = port.readUntil("\n");
// If we actually received something:
if (str.length > 0) {
// Remove extra spaces/newline, then split it into two numbers.
let parts = str.trim().split(",");
// Make sure we really got two numbers before using them.
if (parts.length === 2) {
xVal = int(parts[0]); // Convert the first part to a number.
yVal = int(parts[1]); // Convert the second part to a number.
}
}
// make screen black and clear it.
background(0);
// Convert joystick values (0 - 1023) to screen coordinates
// (0 - width or height).
shipX = map(xVal, 0, 1023, 0, width);
shipY = map(yVal, 0, 1023, 0, height);
// Draw the spaceship at the new position.
fill(0, 255, 0);
drawSpaceship(shipX, shipY);
// draw the obstacle as a red square
fill(255, 0, 0);
rect(250, 150, 100, 100);
// Check whether the spaceship is inside the boundaries of the obstacle.
if (shipX > 250 && shipX < 350 && shipY > 150 && shipY < 250) {
// If the ship just entered collision:
if (!collision) {
port.write("1"); // Tell Arduino to turn the LED ON.
}
collision = true; // Remember the ship is touching the obstacle.
} else {
// If the ship just left collision:
if (collision) {
port.write("0"); // Tell Arduino to turn the LED OFF.
}
collision = false; // No longer colliding.
}
// display joystick values on the screen
fill(255);
text(`Joystick: ${xVal}, ${yVal}`, 70, 10);
// Show either “Collision!!” or “All clear”
text(collision ? "Collision!!" : "All clear", 30, 30);
}
// function to draw a spaceship-looking shape for my game
function drawSpaceship(x, y) {
push(); // Save current drawing settings
translate(x, y); // Move drawing origin to the spaceship location
fill(150, 200, 255); // light blue body
noStroke();
// Main body of the ship (wide horizontal ellipse)
ellipse(0, 0, 40, 20);
// Wings — two small triangles on the sides
fill(100, 150, 255);
triangle(-20, 0, -35, 10, -20, 10);
triangle(20, 0, 35, 10, 20, 10);
pop(); // Restore original drawing settings
}
// Serial Connection Functions
function setupSerial() {
port = createSerial(); // Create a serial port object.
// check if we’ve connected before
let usedPorts = usedSerialPorts();
// If the user connected before, auto-connect to the same port.
if (usedPorts.length > 0) {
port.open(usedPorts[0], BAUD_RATE);
}
// Make the “Connect to Arduino” button.
connectBtn = createButton("Connect to Arduino");
connectBtn.position(10, 10);
connectBtn.mousePressed(onConnectButtonClicked);
}
function checkPort() {
// If the serial port is NOT open:
if (!port.opened()) {
// Update button text
connectBtn.html("Connect to Arduino");
// Gray background and message telling user what to do
background("gray");
fill(255);
text("Click 'Connect' to start", width / 2, height / 2);
textAlign(CENTER, CENTER);
return false; // Tell draw() that nothing should run yet
} else {
// If the port is open, show “Disconnect”
connectBtn.html("Disconnect");
return true;
}
}
function onConnectButtonClicked() {
// If the port is closed, open it.
if (!port.opened()) {
port.open(BAUD_RATE);
// If it’s already open, close it.
} else {
port.close();
}
}